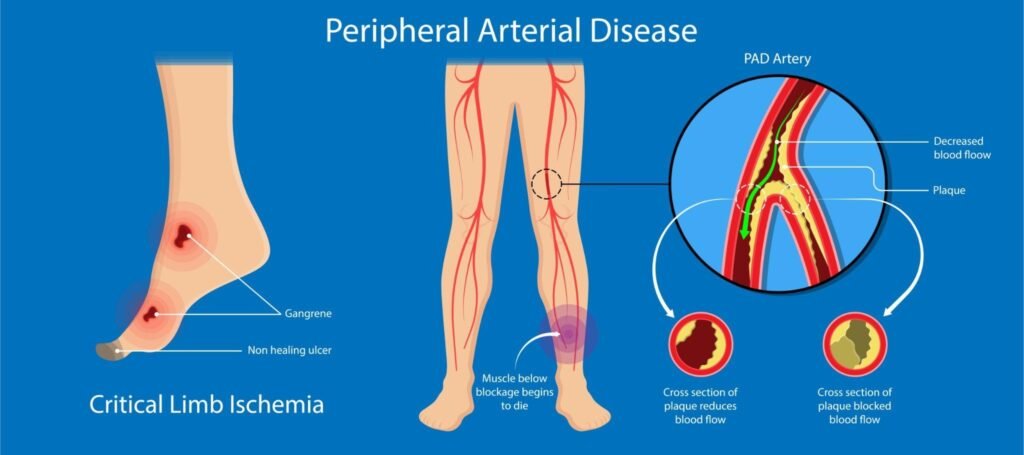
What is PAD?
Peripheral artery disease is a condition that causes the arteries that are located outside the heart, to become narrowed. It is also known as peripheral arterial disease. The narrowing of these arteries causes the affected person to have decreased blood flow to their organs and other tissues. It can cause pain when walking, swelling in your leg muscles and feet, and impaired blood flow to your skin.
PAD can be caused by plaque buildup, smoking, or high blood pressure. It is usually detected through a noninvasive imaging test called an ultrasound. This test is used to detect the narrowing of the artery inside the leg.
How are PAD Risk Factors Determined?
PAD is a condition where peripheral arteries are narrowed or blocked. This can be caused by an injury, weakened blood vessels, smoking, diabetes, high cholesterol levels, and more.
PAD risk factors are determined based on what other diseases a person may have. For instance, if a person has peripheral artery disease, then the risk factors for that person will be determined based on what else they might have. If a person has arterial insufficiency, then the PAD risk factors for that person will be determined by whether or not they have any other diseases.
The most common PAD risk factors are peripheral artery disease and arterial insufficiency. The two often associated diseases with these PAD risks are pulmonary artery disease and critical limb ischemia.
Symptoms of PAD or its Complications?
In peripheral artery disease or PAD, progressive narrowing of the arteries in the legs and feet reduces blood flow. This is a serious condition that may lead to complications including rest pain, ulcers, and gangrene.
The symptoms of PAD can be quite mild or may progress to severe pain that does not go away. Symptoms include:
-Slight discomfort when walking
-Leg cramps
-Aching muscles
-Rest pain
-Numbness in the feet and legs
How is PAD Diagnosed and Treated?
Let’s explore the peripheral artery disease diagnosis and treatment process in-depth.
Now, peripheral artery disease is typically diagnosed by a physician during a medical examination or routine screening. Depending on the patients’ age, family history of heart disease, gender, waist circumference, high blood pressure, high cholesterol level or diabetes status are some of the factors that may lead to further investigation.
A diagnosis of peripheral artery disease (PAD) is usually done through a physical examination and an ankle-brachial index (ABI) test.
The ABI test determines blood flow in the lower body, which can help to rule out or diagnose PAD. The ABI test compares the blood pressure in the ankle and arm. Generally, a reading of less than 0.9 on an ABI test is considered abnormal, but it’s not always accurate for everyone.
The best way to diagnose PAD is via an ultrasound scan of the legs which will allow your physician to see if there are blockages in your arteries. If you have PAD and you are over 50 years old, it can lead to heart attack or stroke which makes it very important to get treated immediately.
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a type of peripheral vascular disease that’s caused by blockages in the arteries to the legs, hip, and pelvis. It can lead to problems such as intermittent claudication and strokes.
Patients with PAD are treated by managing risk factors like smoking and diabetes, exercising, and taking medicines like statins to lower cholesterol.
The treatment of PAD depends on the type and severity of symptoms. The goal is to reduce or prevent leg pain (intermittent claudication), improve walking ability, and prevent leg ulcers, strokes, and heart attacks.
Treatment for PAD includes:
-Losing weight if you’re overweight
-Eating a healthy diet
-Exercising regularly
-Quitting smoking if you smoke
-Medications: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
There are different ways to treat PAD. The preferred treatment depends on the severity of the disease. For mild cases, lifestyle changes or medication may be sufficient. For more severe cases, interventions such as surgery might be needed.
Complications of Unmanaged PAD. How Can it be Managed?
Peripheral artery disease is a common circulatory problem that can affect people of any age. It happens when plaque builds up in the arteries and restricts the flow of blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
Some of the complications that a person with an uncontrolled peripheral artery disease is at risk for are:
– Strokes,
– Angina,
– Heart attack,
– Heart failure,
– Poor circulation of blood in the legs and feet.
The risk of complications increases with age, diabetes, smoking, high blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and chronic kidney disease. Health conditions like these make peripheral artery disease more likely to develop in patients with these conditions. The management of peripheral artery disease is determined by the severity of the condition.
The complications from untreated peripheral artery disease can be life-threatening. If you have peripheral artery disease, it’s important to talk to your doctor about treatment options sooner rather than later.