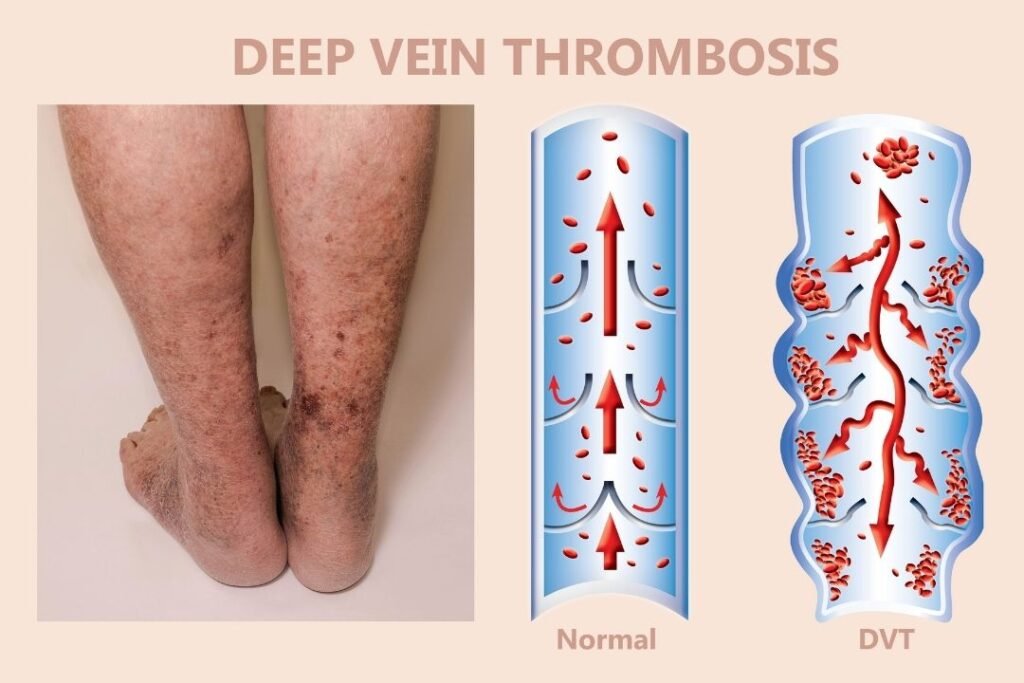
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Deep vein thrombosis is a blood clot that blocks the flow of blood from a vein in the body. It can happen in veins in your lower body, but it can also occur in your veins in your upper body. This blood clot usually forms in the part of your leg below your knee. This clot is called an embolus. When the embolus blocks your blood flow, it’s called a thrombosis.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in a deep vein, usually in the leg. DVT can be very serious. It can form in a vein that returns blood to the heart from a muscle group. It can put pressure on your veins, which can increase your risk of getting an embolism (a blood clot in a vein or artery that travels to another part of your body). DVT can cause complications, like swelling, pain and tissue death.
How DVT Diagnoses are Committed Using a D-Dimer Blood Test and CT Scan?
Diagnosing deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can be challenging, since the condition can mimic other conditions. However, a state-of-the-art test called d-dimer can detect DVT, making it an important tool for diagnosing the condition. During a DVT scan, a doctor may order a d-dimer blood test to detect clots in your body. D-dimer levels rise significantly in DVT, and the d-dimer blood test is often used in conjunction with a CT scan to confirm a DVT diagnosis.
Possible Complications with DVT and How to Prevent Them?
A blood clot in one of the deep veins of the leg is a potentially serious medical problem. It’s known as Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT). DVT occurs when a blood clot forms in one of the deep veins of the leg. When the flow of blood is interrupted, the blood clot can break off and travel to the heart or lungs. While a DVT is usually a temporary condition, it can rarely develop into a life-threatening situation, known as Pulmonary Embolism (PE).
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition, which happens when you develop blood clots in any of your deep veins, usually near your leg. And although the condition is rare, it can develop if you develop an injury or sit in one position for too long. Preventing DVTs requires you to move around for short periods of time, especially while resting, and to move around often when you’re performing more strenuous activities.
Understanding Symptoms & Taking Preventative Measures for DVT
DVT is a blood clot that forms in a deep vein, usually in the leg. It’s most commonly caused by factors that increase the risk of developing blood clots, such as inactivity, prolonged air travel and being immobile. For people who have a prosthetic limb, swelling in the leg may cause DVTs to form in the leg rather than in the artificial limb. Symptoms include pain, tenderness, swelling, redness, warmth, and itching or discomfort in the back of the lower leg. DVTs can cause severe, potentially life-threatening complications, including heart attack, pulmonary embolism, and stroke.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot formed in the deep veins of the body. The risk of DVT increases with age, pregnancy, immobilization, and scleroderma. DVT can cause pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in the affected leg. In the worst cases, DVT can cause pulmonary embolism (PE), which may be fatal. Prevention of DVT is similar to that of PE, including discontinuing smoking, increasing physical activity, and treatment for conditions that cause blood clots, such as varicose veins.
DVT requires immediate medical attention and when it comes to availing reliable DVT treatment in Mumbai, India, there is no better alternative than Dr. Jathin’s Vein Center.
Conclusion: Deep vein thrombosis is less common now than it was in the past, but it is still possible. DVT usually occurs in the legs, and is usually a result of prolonged periods of immobility, such as during a long flight, or a hospital stay. In most cases, the clots dissolve on their own and do not cause lasting damage. However, sometimes a blood clot may break off from its original spot and travel through the bloodstream. This can cause serious problems such as a stroke or heart attack. If diagnosed early, deep vein thrombosis can be treated and most people make a full recovery.