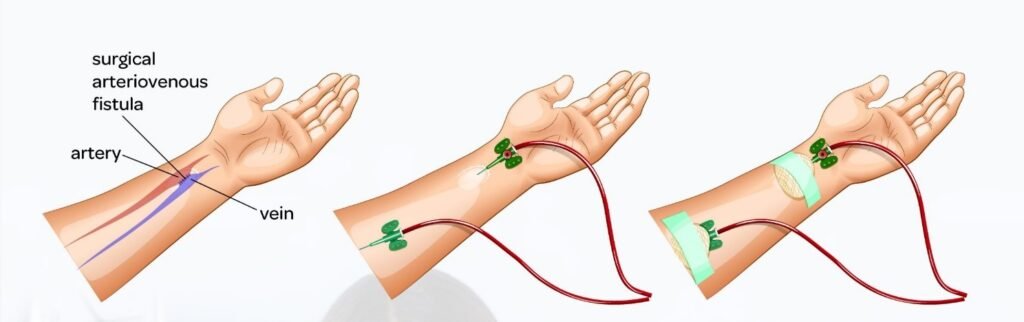
What is an AV Fistula?
A fistula is a passageway between the bowel and bladder, allowing urine from the bladder to leak into the bowel. Fistulas are common during pregnancy because the uterus presses on the bladder and pushes the bladder straight up. Children born with spina bifida often have a fistula, as do people with chronic pelvic inflammatory disease, a complication of a sexually transmitted disease, or an injury or defect in the bladder or bowel.
An Arteriovenous (AV) fistula is a man-made opening in the abdominal wall that connects the umbilicus (belly button) with a blood vessel. A fistula is a hole. The AV fistula lets the dialysis solution flow out of the belly and into the blood.
What is the purpose of an AV Fistula?
An AV fistula is an opening in your chest (thorax), neck, or groin through which a catheter (long flexible tube) is inserted. A catheter is put into your vein and is attached to a dialysis machine to remove waste (toxins), chemicals, and water from your bloodstream. A catheter also can be used to inject medicines directly into your heart.
Why do I need an AV Fistula?
An AV fistula is a surgically created blood vessel that allows blood to flow outside the body through the abdominal wall. The AV fistula is used to treat kidney failure. It can be used for:
- Injecting blood into your body
- Collecting blood
- Collecting urine
- Removing blood
- Removing fluid
Who should get an AV Fistula?
An AV fistula is a hole in the vein between the artery and the vein. It occurs when the vein has been damaged or eroded. This can happen when someone has had vein surgery or if they have a large varicose vein in the leg. It could also be due to a condition called lymphedema. The most common cause of an AV fistula is while having dialysis treatment in the hospital.
How does it work for dialysis?
The AV Fistula is a small device that can be used to deliver dialysis treatments. The device consists of a sheath that fits around the artery, and a needle that is inserted into it. The sheath is connected to a dialysis machine, by means of a tube, where blood is pumped through the sheath and back into the patient’s body. The needle is connected to the sheath; therefore, when you squish the device, the needle moves with it, thus delivering the blood.
The Procedure
Av Fistula is a type of surgical defect characterized by a tunnel or break in the veins of the lower extremity. It can be either partial or complete.The most common cause of av fistula is thrombosis (blood clot), which occurs due to prolonged orthopedic surgery on a joint. When the clot forms in the vein, it enlarges, widens and ruptures the vein. The enlarged vein becomes a hole through which blood escapes from the body.
Are you suffering from av fistula and missing out on daily activities due to its pain? Then, do we have a solution for you. It is the procedure called “av fistula procedure”. It is a non-surgical procedure to end the pain of av fistula by breaking the small blood vessel that is the cause of the pain.
Dialysis is a life-saving treatment for people with kidney failure that allows the body to continue producing fluid and waste. Blood is filtered from the body and placed in the dialysis machine, which processes it and then pumps it back into the body. The process of dialysis can be tedious, but it can also be quite expensive for patients who need it. A new procedure called a fistula—which is a small hole that is made to connect dialysis machine to the patient’s body—has made dialysis more convenient, while also reducing costs.
What are the side effects of an AV Fistula?
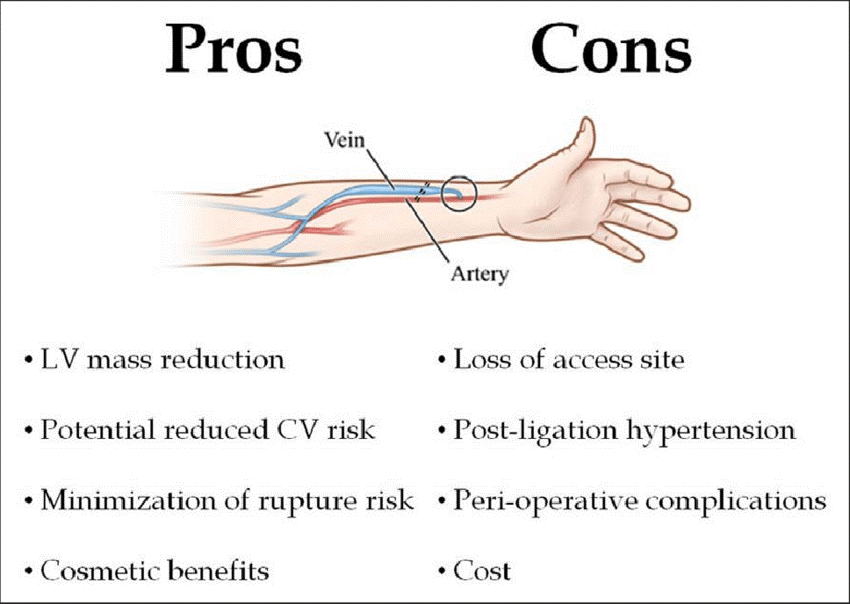
We all have AV fistula defects: a hole in one of the veins that connects our heart to the rest of the body. They can occur in the small and large veins of the legs and arms, resulting in blood leaking into our tissues, or they can occur in the aorta, which can result in the blood pooling in the abdominal cavity. Patients with AV fistulas have a high risk of blood clot formation and blood clots can travel to other parts of the body. If a blood clot travels to the brain, it can cause a stroke or a hemorrhage. If a blood clot travels to other parts of the body, it can cause Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT), a life-threatening condition.
Conclusion
In summary, I believe that fistula should be considered in all patients with renal failure for hemodialysis or for peritoneal dialysis. Fistula should be preferred to the tunneled catheter because of its lower septal morbidity and superior long term patency rate. In addition, fistula should be constructed in the shortest possible time and any attempt at prolonging the procedure beyond a week should be avoided since this results in higher failure rate.
AV Fistula is very useful in a patient with ESRD and poor vein status. The advantages over arteriovenous grafts are easier construction, higher patency and lower cost. Fistulae can be inserted in a day and are easily changed, if needed.